How to Install and Enable the EPEL Repository on AlmaLinux

 8m
8m
 0 comments
0 comments
Understanding EPEL Repository on AlmaLinux: Why It’s More Than Just Extra Packages
If you’ve ever worked with AlmaLinux or any RHEL-based distro, you’ve probably run into a moment where you try to install a tool… and it just isn’t there, the system is lean by design, also great for security and performance, but not so great when you need practical software for development or server management. That’s where EPEL comes in, but here’s the thing: EPEL isn’t just a convenient “add-on repo.” For many sysadmins and developers, it’s the missing half of an Enterprise Linux system.

What EPEL Really is, and Why it Exists?
EPEL stands for Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux, this project is a community-driven project maintained by the Fedora team, offering packages that aren’t included in RHEL, AlmaLinux, or CentOS by default, but this isn’t a random software dump; it’s carefully curated, tested, and designed to work with the base system, not against it, These packages are built using Fedora’s build system, ensuring high compatibility and quality. What you get is the extended functionality of Fedora, but adapted for the stricter, more stable environment of enterprise distros, think of EPEL as a bridge between Fedora’s innovation and RHEL’s rock-solid reliability, for additional Linux tutorials, visit our website.
Why Professionals Trust EPEL on AlmaLinux ( and Why Should You Too)
Here’s where it gets practical: in most real-world scenarios, you’ll eventually need tools like:
- “htop” for monitoring
- “fail2ban” for security
- “certbot” for SSL automation
- “mosh” for better remote access
- “python3-pip” for development
Without EPEL, you’d either have to build these from source or hunt down third-party repos, both of which open the door to dependency or security risks, with EPEL, they’re a single command away, no guesswork, no tweaking, no risk of breaking your system.
The Broader Value of EPEL (Beyond Convenience)
What EPEL really brings to the table is agility; it makes AlmaLinux suitable not just for stable production setups, but for:
- Dev environments where you need tools fast
- Educational systems that require a wider set of packages
- Cloud infrastructure that demands flexibility
It helps you do more, without giving up the stability that makes RHEL-based systems attractive in the first place, Also, because EPEL is community-maintained by Fedora, the same people behind the base tools used by RHEL , so you get peace of mind knowing the packages are built to integrate well and play nice with your system.
How to Install EPEL on AlmaLinux Step-by-Step
Prerequisites:
- AlmaLinux 8
- Root or sudo access
- Internet connection
- System up to date
Step 1: Keep Your System Up to Date
Before adding anything new, it’s smart to make sure your system’s packages are all fresh, this helps avoid strange errors later on, Just run:
sudo dnf update
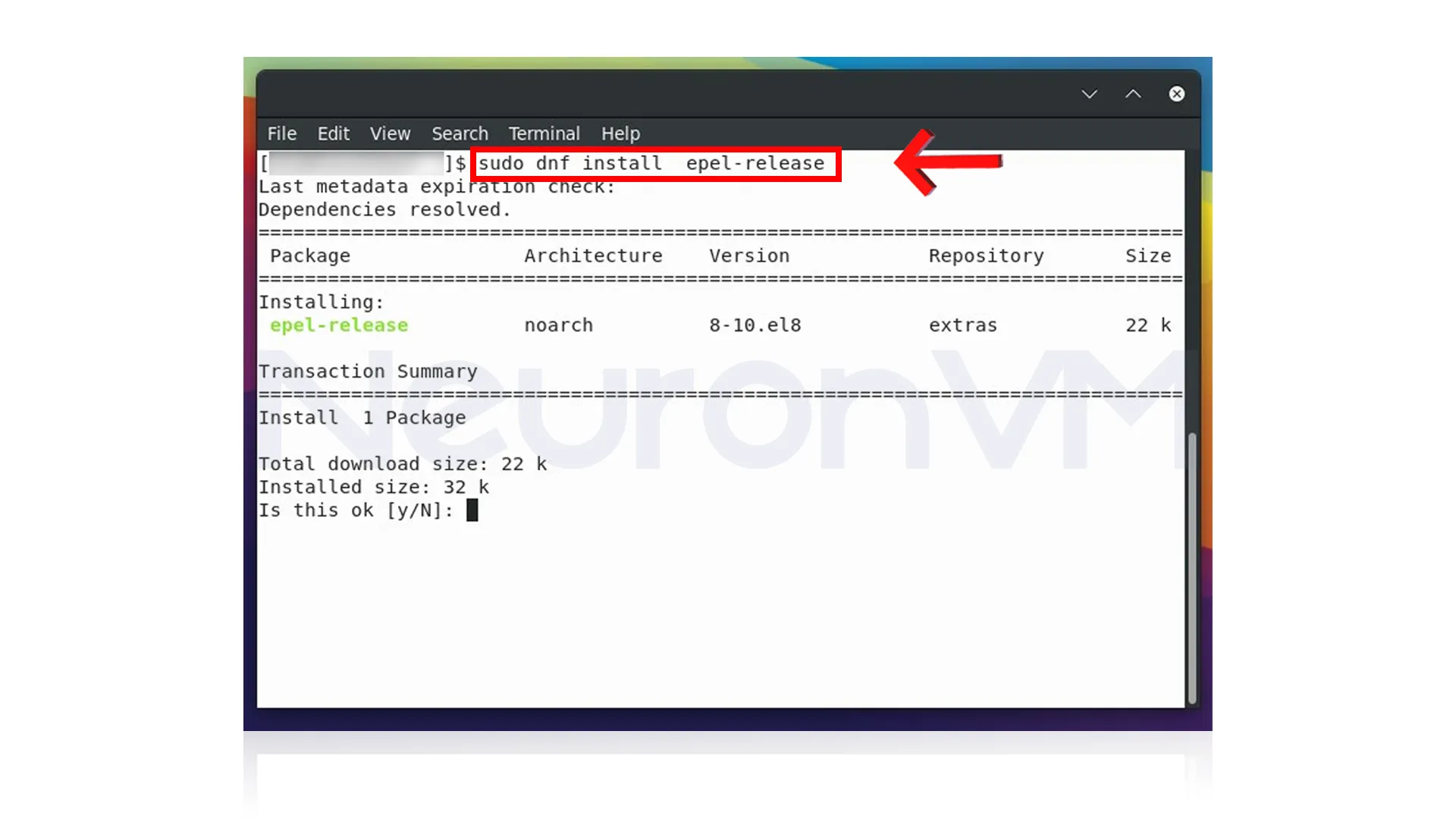
Step 2: Add the EPEL Repository
Next, you want to bring in the EPEL repository to your system, it is as simple as installing a package that sets everything up for you:
sudo dnf install epel-release
Step 3: Confirm the Installation
Want to double-check that the EPEL repo is now part of your system? Use this command to see if the package is there:
rpm -q epel-release
Step 4: Make Sure EPEL Is Enabled
To see if your system is actually using EPEL, run:
sudo dnf repolist epel
If you spot EPEL in the list, you’re all set.
Common Issue: “No Match for epel-release”?
If you see this message, it usually points to one of two problems: either your current enabled repositories don’t include the epel-release package, or there’s a problem with your network connection, first, try running this command again:
sudo dnf install epel-release
If it still doesn’t work, double-check that your AlmaLinux repository mirrors are updated and that your internet connection is stable, Sometimes refreshing your DNS settings or switching to a different mirror can resolve the issue.
Missing Passenger Module (Rare Case)
Some users hit a hiccup involving the Passenger package. If you see dependency issues or failed transactions, it might be resolved with:
sudo dnf install passenger
After that, retry adding the EPEL repository.
Conclusion
If you’re running AlmaLinux in a production environment, not using EPEL is almost like leaving tools in the box, it’s not just about convenience, it’s about efficiency, reliability, and access to software that the broader Linux ecosystem depends on. EPEL isn’t a shortcut, it’s a best practice, and once it’s enabled, you’ve opened the door to a much more flexible and capable server setup.
No, after installation, it will be active until you deactivate it manually.
Yes, you can remove it by using a special command.
You might like it

Ubuntu Tutorials
Introduction and How to use Iftop on Ubuntu 20.04

Kali Linux Tutorials
How to Install and Enable XRDP on Kali Linux

Linux Tutorials
How to Exit Bash Scripts on Errors (Exit Codes, set -e, trap...