How to Install and Configure Gradle on Fedora 33

 7m
7m
 0 comments
0 comments
Gradle is a powerful build tool that supports popular languages and technologies such as Java, Kotlin, C/C++, Groovy, and even JavaScript. It is especially useful in official Android development, and because it is open source, it provides the ability to customize and also automate projects, on this article, in addition to teaching you how to install and configure Gradle on Fedora 33, we will review professional tips and real-world examples of its use.
Prerequisites
To use Gradle, you must have Java version 8 or higher installed on your system. To install Java 8 on Fedora 33:
Other tools needed for
sudo dnf install java-1.8.0-openjdk
java -version
Other tools needed for this tutorial:
sudo dnf install unzip wget
You can use Linux VPS services with different locations to test and develop your projects.
Installing Gradle on Fedora 33
1- Download Gradle from the official page or use the following command:
wget https://downloads.gradle-dn.com/distributions/gradle-6.3-bin.zip
2- Extract the file and move it to the desired path:
unzip gradle-6.3-bin.zip
sudo mv gradle-6.3 /usr/local/gradle
3- PATH configuration:
vim /etc/profile.d/gradle.sh
4- Add the following line to the created :
export PATH=/usr/local/gradle/bin:$PATH
5- Apply changes:
source /etc/profile.d/gradle.sh
gradle --version
The output will be as follows:
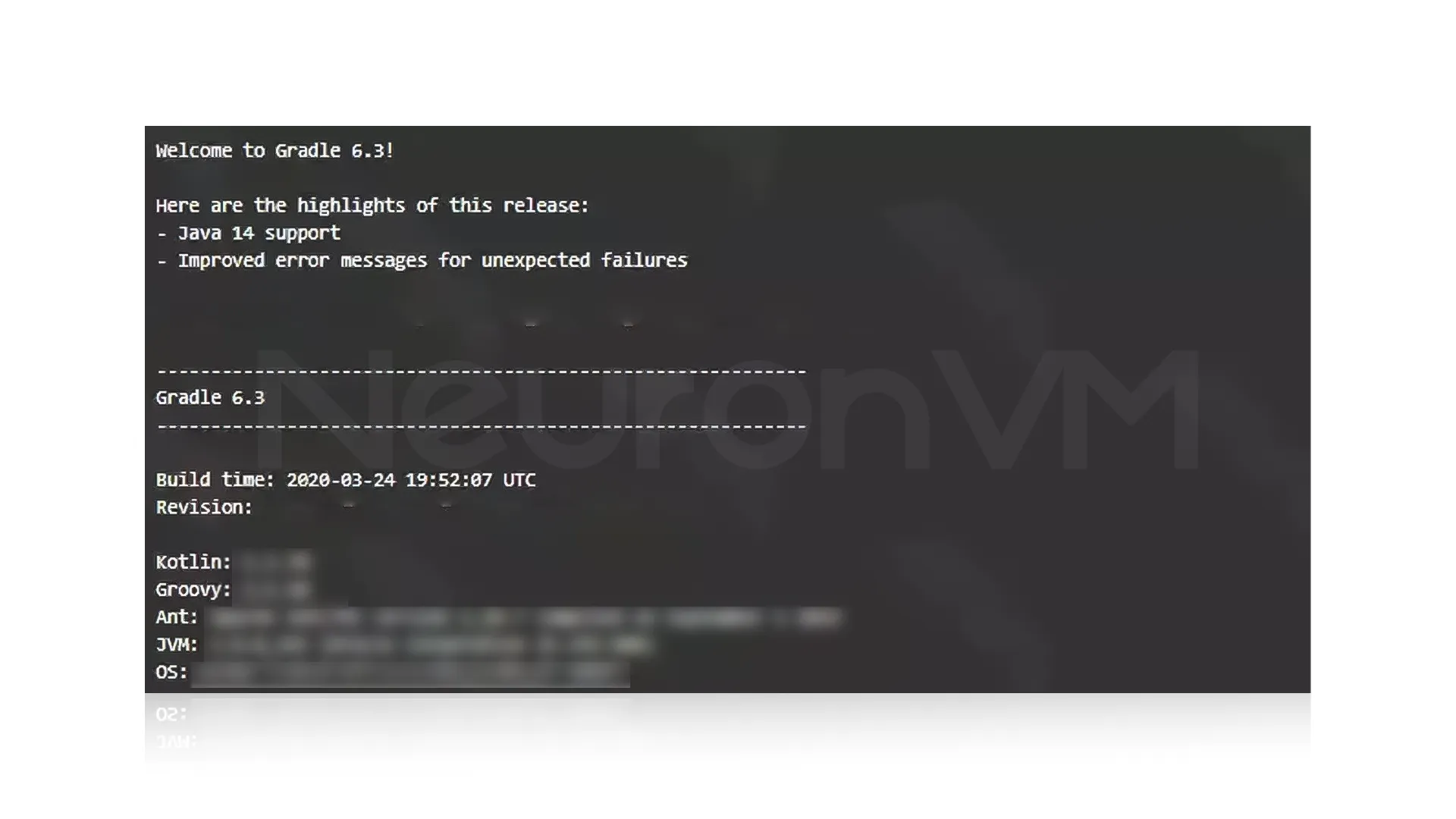
The output indicates that Gradle is installed correctly on your system.
Why is Gradle better than other tools?
One of the most important reasons for Gradle’s popularity over tools like Maven or Ant is its high flexibility. Gradle uses a scripting language based on Groovy and Kotlin, which allows for advanced automation and fine-tuning of the project build process. Unlike Maven, which has a fixed structure, Gradle can dynamically manage complex and multi-module dependencies, significantly increasing build speed and scalability in large projects.
Gradle’s Role in DevOps Processes
In recent years, Gradle has become a key tool in DevOps processes, and development teams can automate the process of testing, building, and also deploying software by integrating Gradle with tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, and GitLab CI, features like Build Cache and Parallel Build make building projects in different environments faster and minimize release times.
Performance Optimization with Build Cache
One of Gradle’s main strengths is its focus on performance optimization, features such as Incremental Build and Smart Caching prevent repetitive tasks from being re-executed, and by that it reduces build times by a factor of 10, using the Gradle Daemon also helps keep background processes running and then execute commands faster.
Pro and Advanced Tips
Java Environment: Make sure JAVA_HOME points to the correct Java path.
Dependency Management: Gradle supports internal and private registries.
Optimize Large Projects: For multi-module projects, use the Gradle Wrapper feature so that all developers have the same version.
Scripting: Automate Gradle and dependency installation and updates by writing Bash scripts.
Common Issues and Solutions
Java Compatibility
Make sure that your Java version is compatible with Gradle, and then that JAVA_HOME is set properly.
Proxy Settings
In environments with a firewall or even proxy, check the gradle.properties file to configure the proxy, and then download dependencies.
Project Script Errors
Is your Build Script giving errors? Then check your build. Gradle settings and plugin versions.
File Access
Check the read/write permissions for the Gradle installation path and also the user directory.
Antivirus and Security Software
Some security software may interface with Gradle functionality, temporarily disable it if necessary.
Real-world example of Gradle usage
An Andrid development team with a multi-module project uses Gradle Wrapper and then local caches to reduce build time, with proper configuration and use of Gradle Daemon, the project’s build time has been reduced from 15 minutes to less than 5 minuets, while dependencies and plugins are managed unchanged, this example shows that Gradle is not just a build tool, but plays a key role in optimizing the devlopment proccess.
Conclusion
Gradle is a flexible and powerful tool that can be used beyond Android development for a variety of Java, Kotlin, C/C++, and even JavaScript projects, the proper installation and configuration on Fedora 33 will increase the speed and automation of projects, with the help of professional tips and best practices, you can use Gradle not only as a build tool, but also as a powerful management solution for large and team projects.
No, Gradle also supports different languages like Java, Kotlin, and C++.
Due to the use of caching and dynamic build system, Gradle is faster than Maven.