How to Install Drupal on Debian: A Practical, Real-World

 9m
9m
 0 comments
0 comments
If you want to build a powerful, secure, and flexible website on Debian, choosing Drupal is always a good idea. In this guide, I’ll walk you through the process from scratch to the Drupal dashboard in a simple, human-like manner, just like I’ve experienced myself installing it on different servers. Drupal is a highly professional, open-source CMS that’s great for large, enterprise-level sites and projects that require complex structures. So if you’re looking for a hassle-free, streamlined installation, this guide is all you need.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure that:
Debian 10 is installed on your server
You have sudo or root access
The server is freshly installed (recommended but not required)
Step 1: Update the System
It is always a good idea to update your packages before any major installation on Debian to avoid bugs and issues from older versions.
apt update -y apt upgrade -y
Step 2: Install MariaDB
Drupal needs a database to store its data. MariaDB is the best and lightest option for Debian. After installation, be sure to secure the database system with its built-in security tool.
apt install -y mariadb-server mariadb-client
This tool allows you to:
- – Set the root password
- – Remove anonymous users
- – Disable remote root access
- – Delete the test database
This part may take a while, but without it, Drupal’s security remains completely vulnerable.
Create a Drupal database
After securing it, create a new database and a dedicated user for Drupal. This is one of the most important parts, as separating users increases security.
mysql -u root -p CREATE DATABASE drupal; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON drupal.* TO 'drupal'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY "StrongPassword"; FLUSH PRIVILEGES; \q
Step 3: Install PHP
Drupal requires a set of PHP plugins and modules to run. By installing the recommended packages, Drupal will work without any problems.
apt install php php-{cli,fpm,json,common,mysql,zip,gd,intl,mbstring,curl,xml,pear,tidy,soap,bcmath,xmlrpc}
By default, PHP for Drupal should include the following:
- – mbstring
- – curl
- – xml
- – gd
- – intl
- – json
- – soap
- – bcmath
Finally, set the timezone and memory limit in the php.ini file to avoid strange bugs during installation (one of the most common installation problems).
vi /etc/php/*/apache2/php.ini memory_limit = 256 date.timezone = America
Step 4: Installing Apache
To run Drupal, Apache is one of the most popular web servers on Debian. After installation, you need to enable a few essential modules, such as rewrite, as Drupal needs it to manage links.
apt install apache2 libapache2-mod-php
Step 5: Download and Install Drupal
Go to the official Drupal website and download the latest version. Then, move the file to the web server path (usually /var/www/html/).
Next:
- – Set the permissions
- – Set the ownership of the files to Apache
- – Create a Virtual Host for the site
Here comes one of the most important installation steps: Configuring Apache to run Drupal properly.
VirtualHost settings include:
- Introducing the domain
- Defining the site’s root directory
- Enabling Rewrite for links
- Setting the necessary permissions
After activating the site and restarting Apache, it’s time to install it via the browser.
Step 6: Install Drupal on Debian via Browser
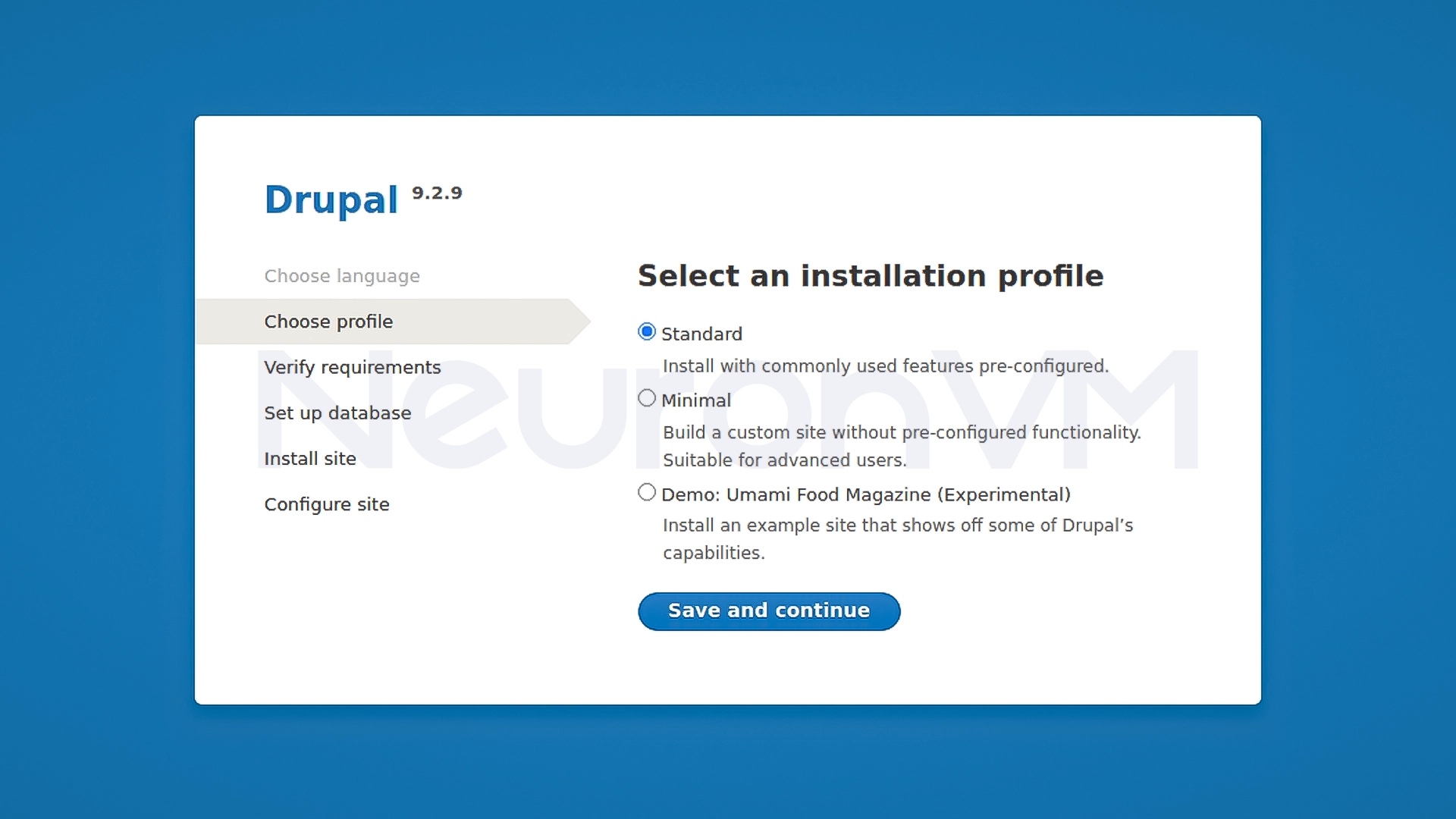
Now enter your domain or IP address in the browser. The Drupal installation page will appear. The steps are as follows:
1- Select installation profile
2- Enter database information
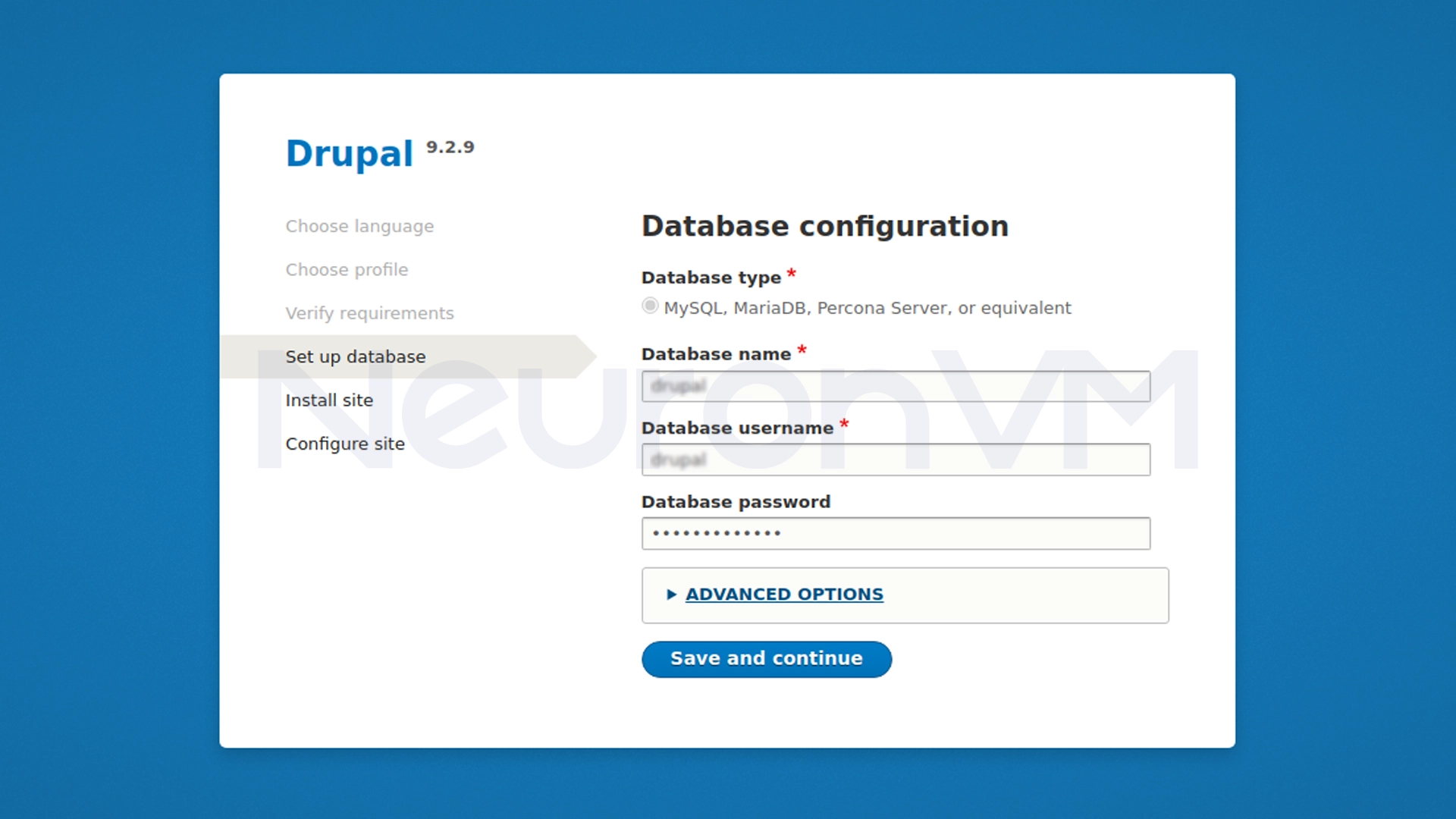
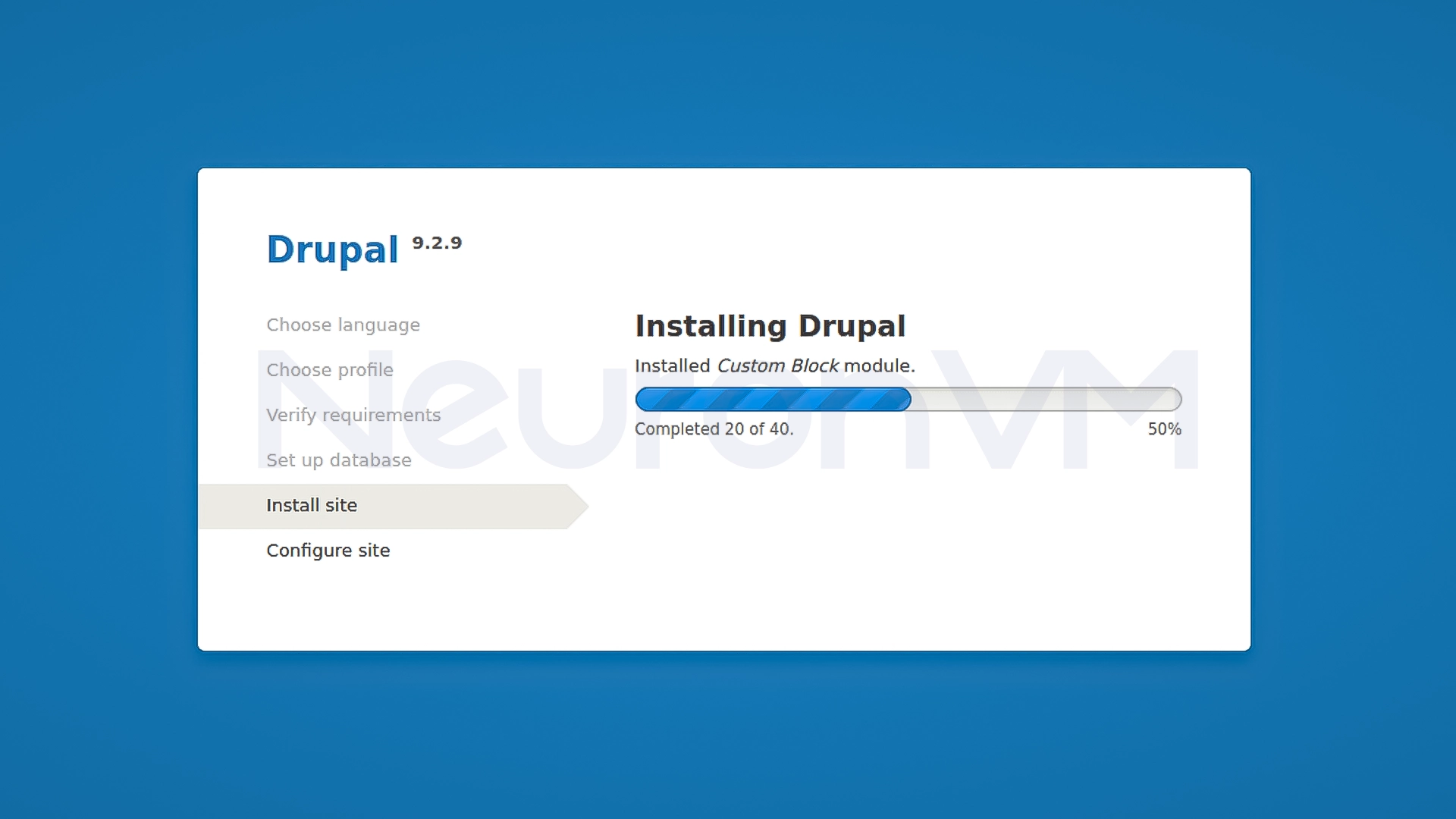
3- Wait for installation
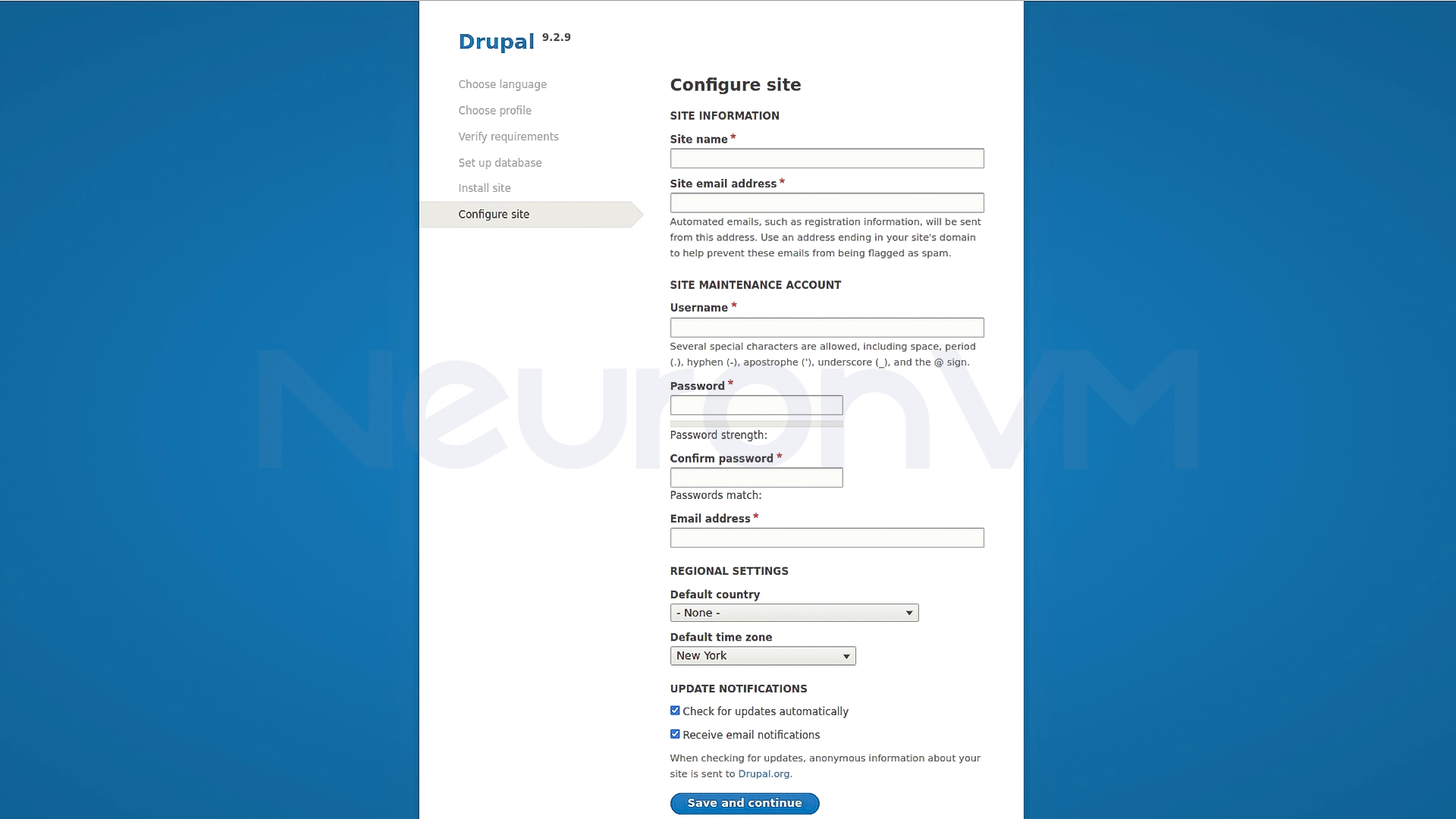
4- Create site administration account
5- Log in to the Drupal panel
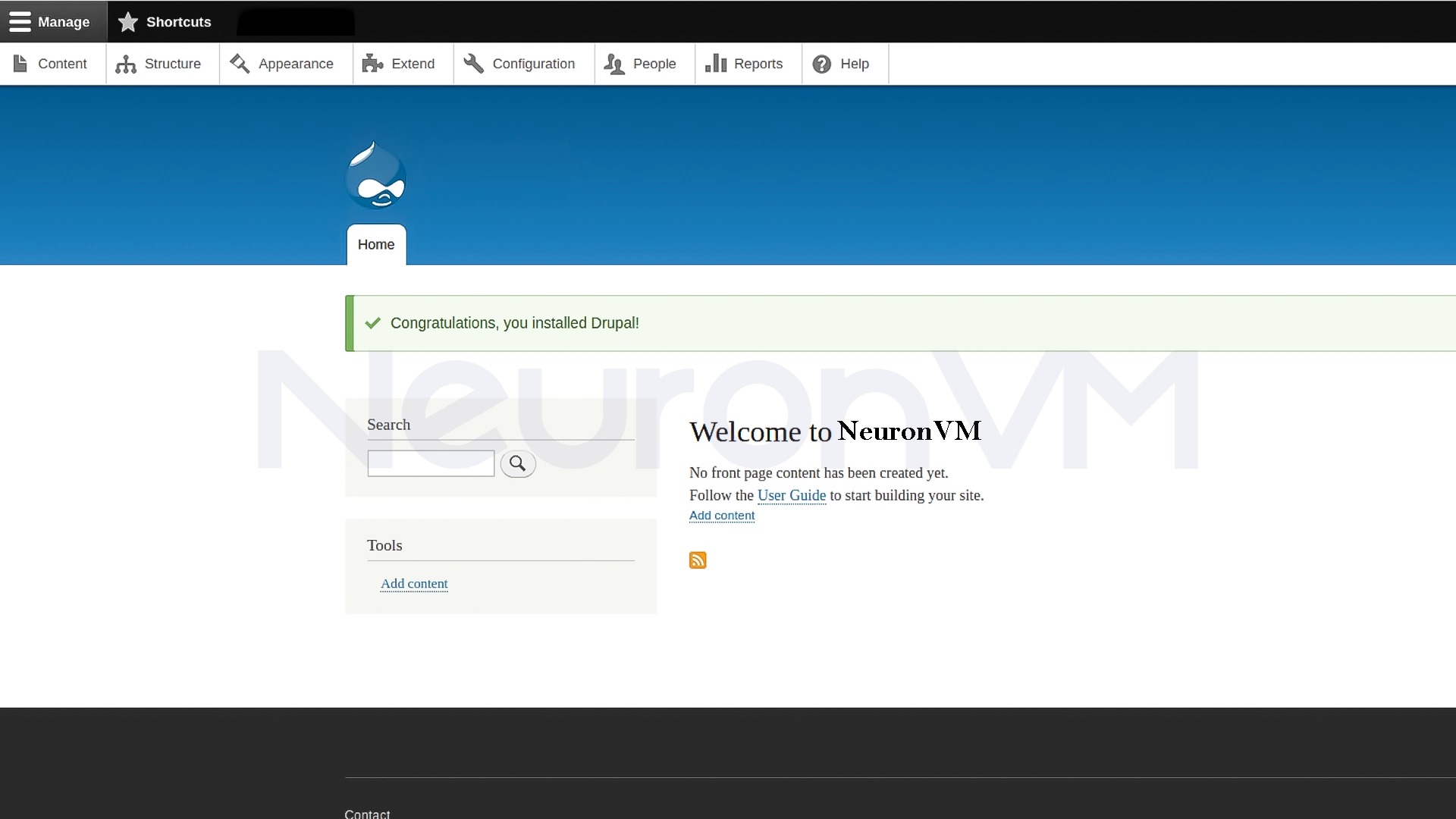
After a few moments, the beautiful Drupal dashboard will appear in front of you.
My personal experience install Drupal on Debian
I’ve been working with Debian for years now, and Drupal is just one of those CMSs that is prone to errors if the prerequisites are not followed exactly, so based on my experience, here are a few key points:
- – If the timezone is not set in PHP, you may get strange errors during the final installation phase.
- – It’s best to create a separate user for the database; using root is always risky.
- – If the rewrite module is not enabled, the site’s pages will not load properly.
- – If your server is light, Drupal will be a little slow during the installation phase, which is normal.
These may seem simple, but they are exactly the things that can save you hours of trouble.
Conclusion
Install Drupal on Debian may seem like a multi-step and time-consuming process at first sight, but once you follow the steps and follow a clear path like this one on our website, it’s quite simple and manageable, In this process, you’ve updated the system, created a secure database, configured PHP and Apache, and finally got Drupal running on your web server. Now you have a powerful, flexible, and stable CMS ready to go on Debian, a completely standard and secure foundation on which you can build a professional, corporate, or large project website. From this point on, Drupal’s capabilities are almost limitless, you just need to specify your site structure, theme, modules, and project needs to get the most out of this system.
No. If you follow the steps step by step, it is quite doable and does not require advanced knowledge.
Usually, the latest versions of PHP 7.4 or 8 or later are recommended to ensure full compatibility and security.
Yes. Just set up an Apache Virtual Host and point the domain to the server.
You might like it