How to Open Ports in Linux Safely (UFW, Firewalld, iptables)
 8m
8m
 0 comments
0 comments
Managing network access is a fundamental skill for Linux users, whether you’re deploying a home server, configuring remote access, or running containers, this 2025 expert guide goes beyond the basic steps and dives into why, when, and How to Open Ports in Linux Distributions securely and efficiently, while there are many tutorials out there, most simply list commands without context, Here, we combine real-world scenarios, best practices, and distribution-specific guidance to help you open ports confidently and securely, learn more on our website.

Why Opening Ports in Linux Still Matters in 2025
It is better to know that even in 2025, knowing how to open ports in Linux is still important, because open ports let apps like Nextcloud, Docker, or WireGuard VPN connect and work properly, but opening a port isn’t just about running a command; it also means making sure only the right people can access it, if you don’t set up rules or keep an eye on it, an open port can become a security risk.
Expert Tip: In today’s modern systems, like cloud-based setups open ports aren’t just controlled by the server, because tools like Kubernetes often handle which ports are open, this means you need to manage traffic rules as part of your automated workflows, like when you’re building or updating your apps,security needs to be built into that process from the start.
Step 1: Checking for Open Ports in Linux
I think it is better before you open any ports, it’s a good idea to see which ones are already in use or listening for connections, to check for a specific port:
netstat -na | grep :[port-number]
If you want to view all listing ports:
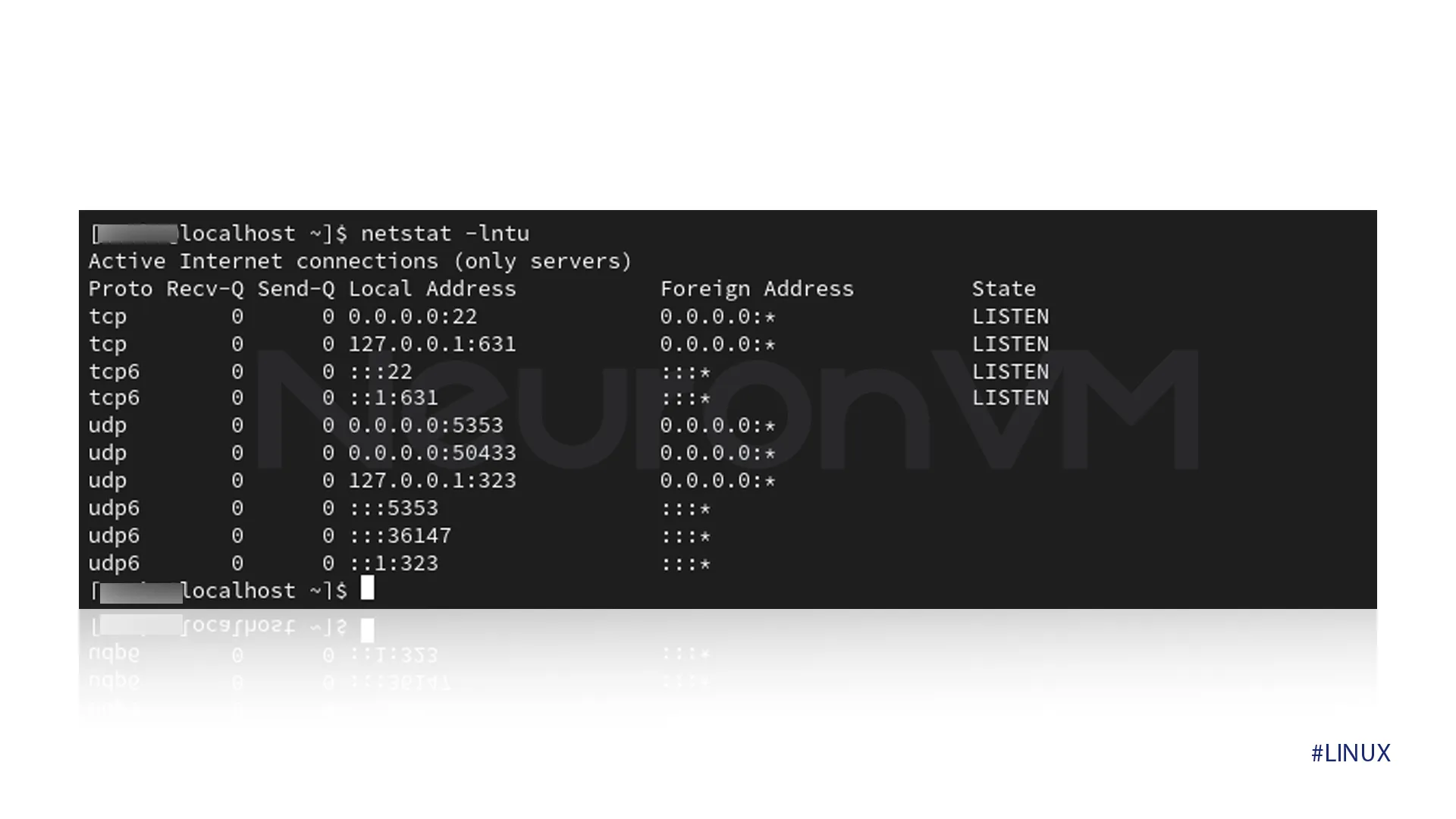
netstat -lntu
The output should look like this.
 Or the more modern:
Or the more modern:
ss -lntu
Tip: ‘ss’ is faster and more accurate than netstat on newer systems, combine it with -p to see associated processes.
Step 2: How to open ports-The Right Way for Your Distro
Not all Linux systems handle firewalls the same way, depending on which distribution you’re using, the method to open ports can vary, here’s how to do it based on your setup.
Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Pop!_OS (UFW
UFW will make things easy to use, which makes it a great choice for personal servers or anyone just getting started with firewalls.
Basic Port Open:
sudo ufw allow [port-number]
Open by Service:
sudo ufw allow [service-name]
Firewalld (CentOS, RHEL, Fedora)
Firewalld uses dynamic zones and services, which will offer you more granularity, to do that:
Open a Port:
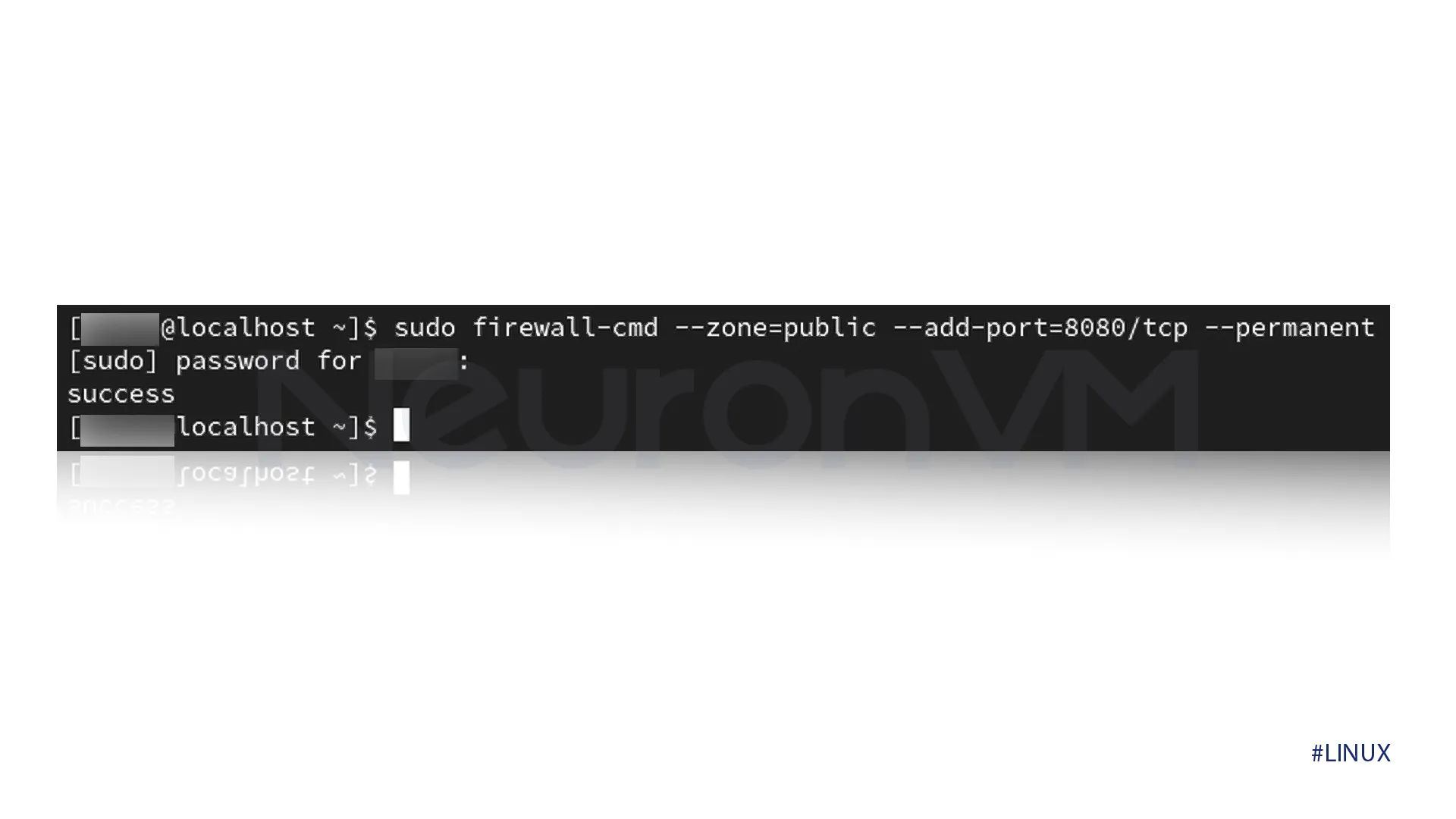
sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=[port-number]/[protocol] --permanent
The output should look like this.
 iptables (custom environments):
iptables (custom environments):
For more control or when UFW/Firewalld aren’t available, iptables is still the go-to tool for custom rules.
Allow Port for IPv4:
To allow port for IPv4,
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p [protocol] --dport [port] -j ACCEPT
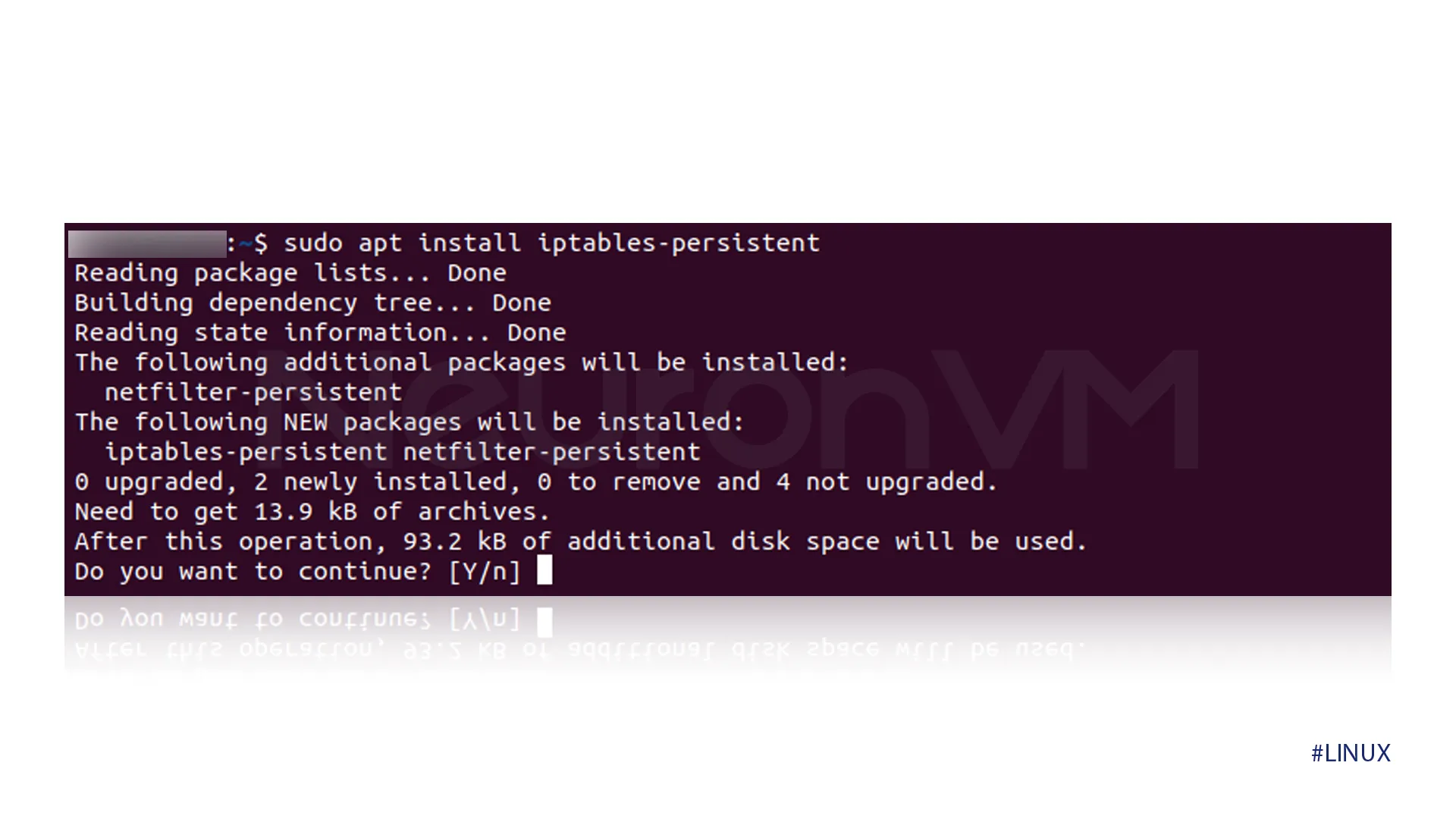
On Debian-based systems, you need to save the rules we have made by entering this command, With iptables, you have a lot of control, but it’s not very beginner-friendly, if you make a mistake, you could block SSH and lose access to your server, always test your rules carefully.
iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4
Step 3: Verifying That the Port is Open
Once a port is open, confirm it’s actually reachable, locally and remotely.
List All Open Sockets:
ss -lntu
Scan your own server:
nmap localhost -p 8080
If you want Remote Testing: Just swap out ‘localhost’ with your server’s public IP address, but don’t forget to check that your router or cloud firewall is actually forwarding the port
Real-World Use Cases
Here’s where this matters:
- Game Servers: Open UDP 27015 for Steam-based games.
- Nextcloud or Web Servers: Open 443/TCP for HTTPS.
- Remote Work Access: Open 51820/UDP for WireGuard VPN.
- Docker or K8s Environments: Use firewall rules to isolate containers across networks.
- Best Practice: Never expose a service unnecessarily, se port knocking, VPNs, or jump hosts, when security matters.
Conclusion
This guide showed you how to open a port in Linux using UFW, Firewalld, and iptables. But more importantly, we emphasized why to open a port and how to do it safely, as systems become more interconnected and attack surfaces grow, understanding the full context of your network rules is no longer optional; it’s essential. Have a complex setup or need help troubleshooting? Our Linux experts are available to help you audit and secure your network configuration, bookmark this guide, and explore our full collection of real-world Linux tutorials to level up your sysadmin skills.
It allows incoming network connection.
HTTP, HTTPS, SSH, FTP